Acupressure Points for Calming the Mind
In Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), a calm and peaceful mind is a reflection of balanced internal organ function and harmonious flow of Qi and Blood. The Shen (spirit/mind) resides in the Heart (Xin) and is nourished by the Heart Blood, Kidney Essence, and supported by the Liver, Spleen, and Lung systems. When these organs are imbalanced, the Shen becomes unsettled—manifesting as anxiety, overthinking, restlessness, irritability, poor concentration, and insomnia.
Unlike modern medicine that treats mental restlessness as isolated psychological symptoms, TCM views it as a holistic imbalance involving both emotional and physiological aspects. Acupressure is a simple yet powerful tool to regulate Qi, soothe emotions, and bring peace to the mind.
Key Organ Systems Involved
- Heart (Xin)
- Houses the Shen (spirit).
- Imbalance leads to anxiety, insomnia, palpitations, and agitation.
- Kidney (Shen)
- Anchors the Heart through Yin and Essence.
- Deficiency results in fear, panic, and chronic anxiety.
- Liver (Gan)
- Regulates emotional flow and Qi movement.
- Stagnation leads to frustration, irritability, and mood swings.
- Spleen (Pi)
- Governs thought and produces Blood.
- Deficiency causes overthinking, obsessive worry, and fatigue.
- Lung (Fei)
- Affects sadness and emotional release.
- Weak Lung Qi leads to low mood and grief.
Common TCM Patterns for Mental and Emotional Disturbances
- Heart Yin Deficiency
- Symptoms: restlessness, palpitations, insomnia, dry mouth, vivid dreams
- Tongue: red, peeled tip
- Pulse: thin and rapid
- Heart and Spleen Qi Deficiency
- Symptoms: overthinking, poor memory, fatigue, palpitations, dream-disturbed sleep
- Tongue: pale with teeth marks
- Pulse: weak
- Liver Qi Stagnation Transforming to Heat
- Symptoms: irritability, mood swings, chest tightness, poor sleep
- Tongue: red sides
- Pulse: wiry and rapid
- Heart and Kidney Disharmony
- Symptoms: anxiety, tinnitus, night sweats, insomnia, low back ache
- Tongue: red and dry
- Pulse: thin and rapid
Treatment Principles in TCM
- Nourish Heart Yin and Blood to anchor the Shen
- Harmonize Heart and Kidney to support emotional grounding
- Regulate Liver Qi to release emotional tension
- Tonify Spleen Qi to support mental clarity and reduce worry
- Anchor the Shen through stabilizing Qi and calming internal Heat
Diet and Lifestyle Tips (TCM-Based)
Diet Tips
- For Heart Yin deficiency: consume black sesame, tofu, lily bulbs, goji berries
- For Spleen Qi deficiency: eat warm cooked meals like oats, pumpkin, sweet potatoes
- For Liver Qi stagnation: include green vegetables, citrus, peppermint tea
- Avoid stimulants (coffee, alcohol), spicy food, and late-night eating
- Drink herbal teas with suan zao ren (jujube seed), longan fruit, and chamomile
Lifestyle Tips
- Sleep before 11 PM to support Heart and Gallbladder
- Practice deep breathing, meditation, or Qigong daily
- Avoid emotional suppression—journaling or talking can help
- Reduce screen time and mental overstimulation before bed
Daily Acupressure for Calming the Mind
Here are 5 acupressure points known in TCM to calm the mind:
- HT7 – Shen Men (神門)
- Location: On the wrist crease, radial side of the flexor carpi ulnaris tendon
- Function: Calms the Shen, nourishes Heart Blood, alleviates anxiety and insomnia
- PC6 – Nei Guan (內關)
- Location: 2 cun above the wrist crease, between two tendons
- Function: Opens the chest, calms the Heart, soothes emotional distress
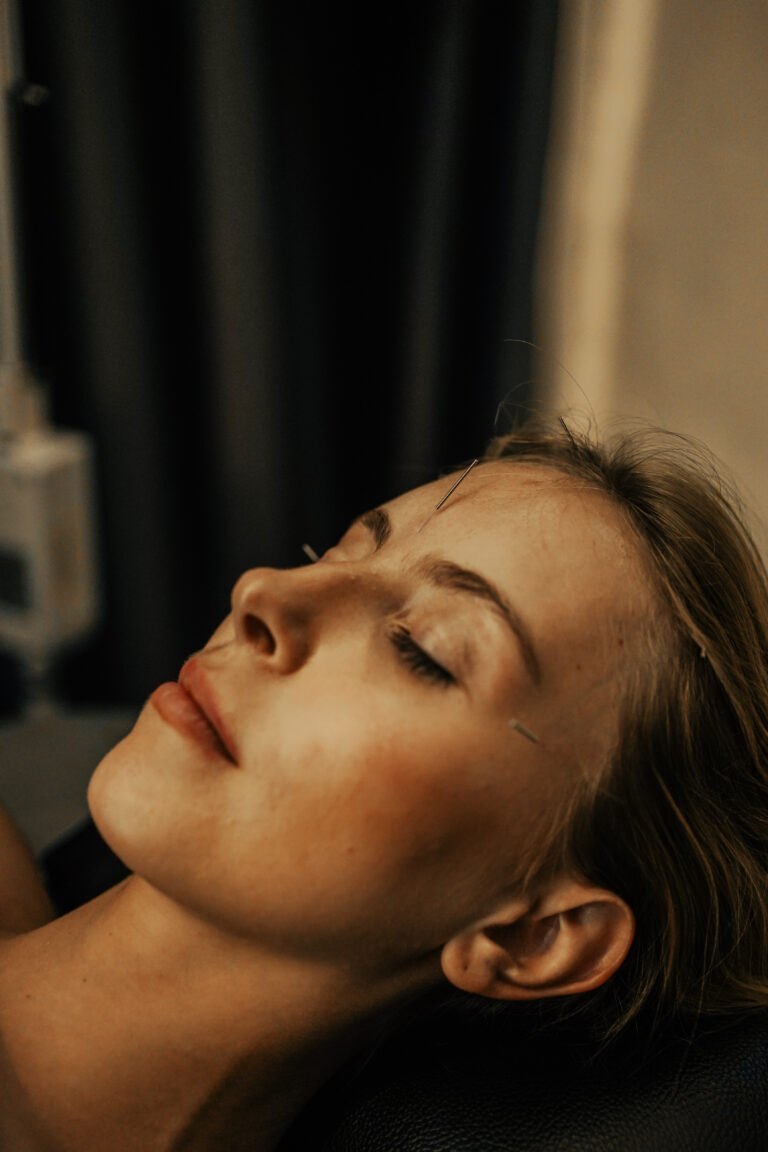
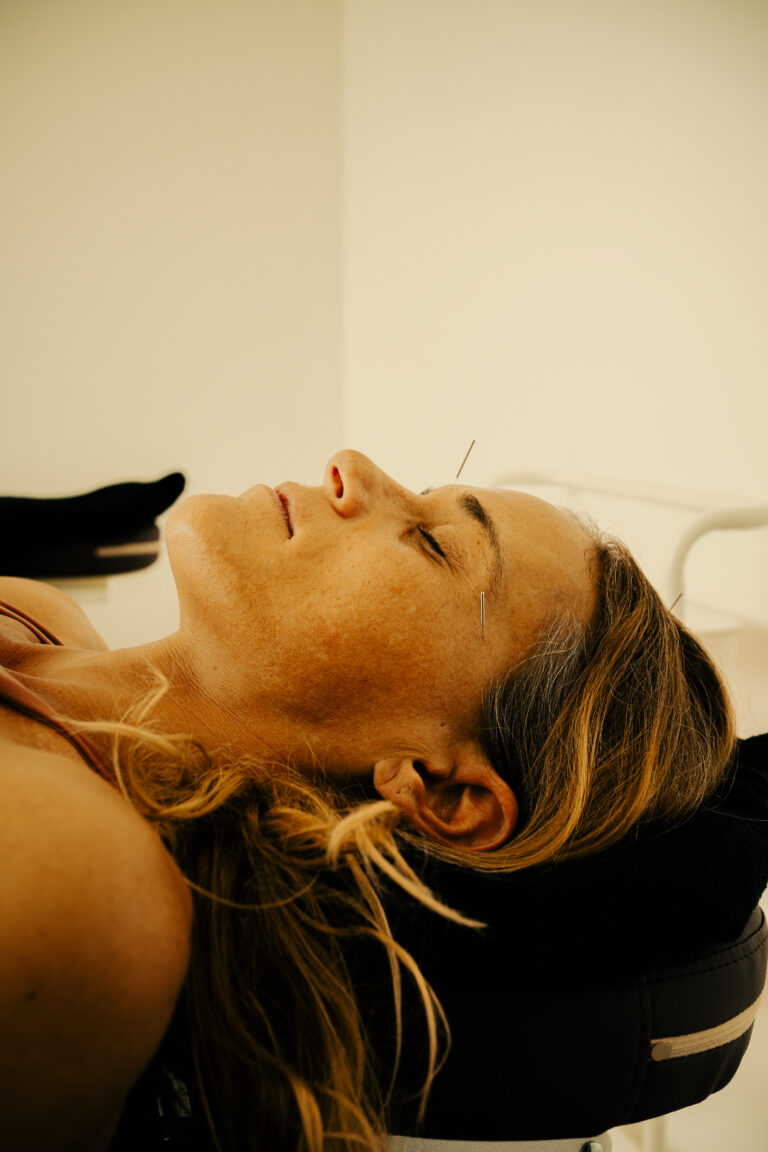
- Yin Tang (印堂)
- Location: Midpoint between the eyebrows
- Function: Relieves stress, calms the mind, clears frontal headaches
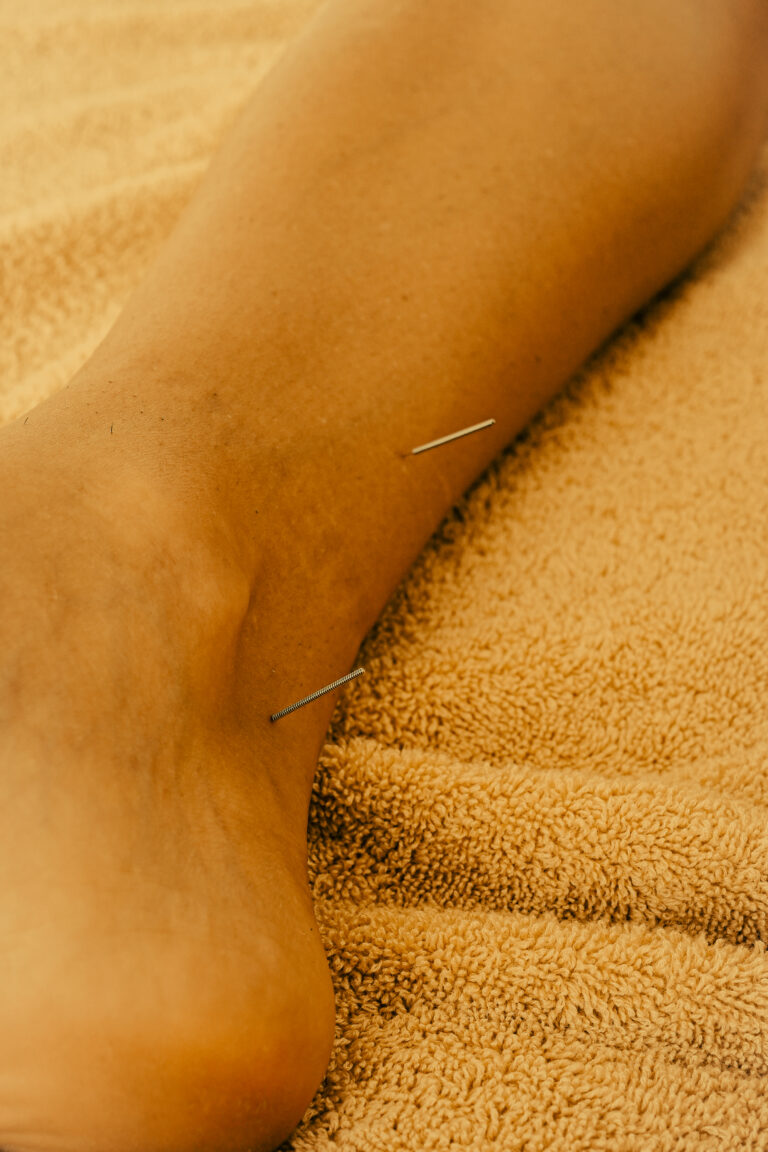
- SP6 – San Yin Jiao (三陰交)
- Location: 3 cun above the medial malleolus, behind the tibia
- Function: Nourishes Liver, Spleen, and Kidney; stabilizes emotions and sleep
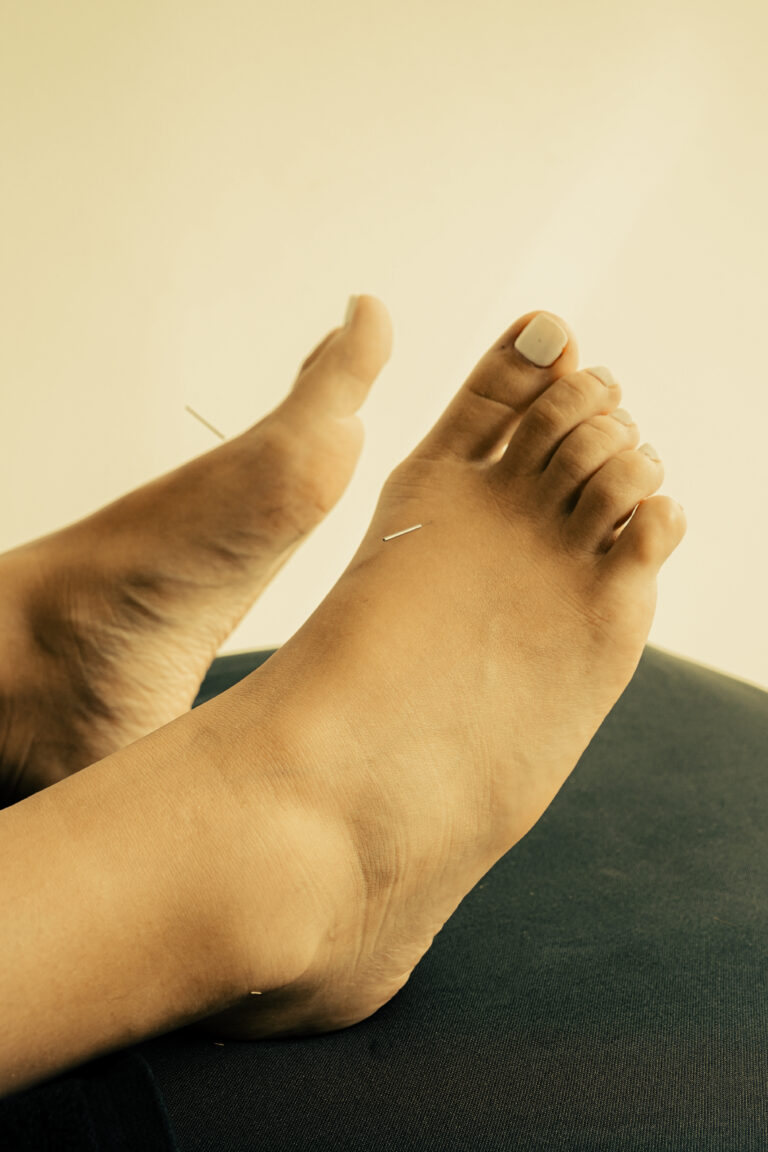
- KD1 – Yong Quan (湧泉)
- Location: On the sole of the foot, in the depression below the ball of the foot
- Function: Grounds the Shen, calms fear, anchors overactive Yang energy
How to use:
Press each point gently with the thumb or index finger for 1–2 minutes, preferably during the evening while breathing deeply.
TCM Treatment Recommendation
- Acupuncture therapy to calm the Shen and regulate affected organs
- Focus points: HT7, PC6, Yin Tang, SP6, LV3, KD3
- Auricular acupuncture: Shen Men, Heart, Brain, and Point Zero
Conclusion
The mind cannot be truly calm without a harmonious body, and TCM provides a unique roadmap for achieving both. By addressing the root causes of emotional restlessness—whether it’s Yin deficiency, Liver Qi stagnation, or Heart–Kidney disharmony—we can restore clarity, inner peace, and restful sleep. Daily acupressure, dietary support, and gentle lifestyle practices offer simple yet profound tools to support mental health—naturally and holistically.
Sources
- Maciocia, Giovanni. The Practice of Chinese Medicine: The Treatment of Diseases with Acupuncture and Chinese Herbs. Elsevier, 2005. ISBN: 9780443074905
- Deadman, Peter, Al-Khafaji, M., Baker, K. A Manual of Acupuncture. Journal of Chinese Medicine Publications, 2007. ISBN: 0951054651
Chen, John K. & Chen, Tina T. Chinese Medical Herbology and Pharmacology. Art of Medicine Press, 2004. ISBN: 9780974063504